原文标题:Money Talks: The Environmental Impact of China’s Green Credit Policy
原文作者:Sun, Junxiu,Wang, Feng,Yin, Haitao,Zhang, Bing
发表期刊:Journal of Policy Analysis and Management
关键词:信贷控制 环境规制
一、研究背景
中国实行的绿色信贷政策,是利用环保相关部门的有效信息,对环境不良企业实行信贷限制,对环境友好型企业给予信贷支持。该政策的实施,可以促使企业更有内在动力进行绿色生产和创新。因此,绿色信贷政策被视为对中国现有环境监管体系的重要补充。本文作者对绿色信贷政策控制环境污染有效性进行了研究,重点是哪种类型的企业对该政策的反应更积极,以及在该政策下企业倾向于采取哪种类型的环境行动。这项研究的目的是确定该政策是否导致了企业污染行为的自愿改变以及如何改变。
二、研究设计
作者选取江苏省江阴市为研究对象,运用合成控制法,构造合理的对照组,并利用DiD方法对绿色信贷政策的实施效果进行研究。
由于江阴市是县级市,作者基于江苏省所有其他17个县级市构建了2000年至2007年的年度县级面板数据库。之所以选择2000年作为起始年份,是因为2000年是第一个包含所有县级城市污染数据的年份;样本期结束于2007年,是因为2007年是全国绿色信贷政策公布的年份,此后,17个县级城市不具备成为潜在控制组的条件。
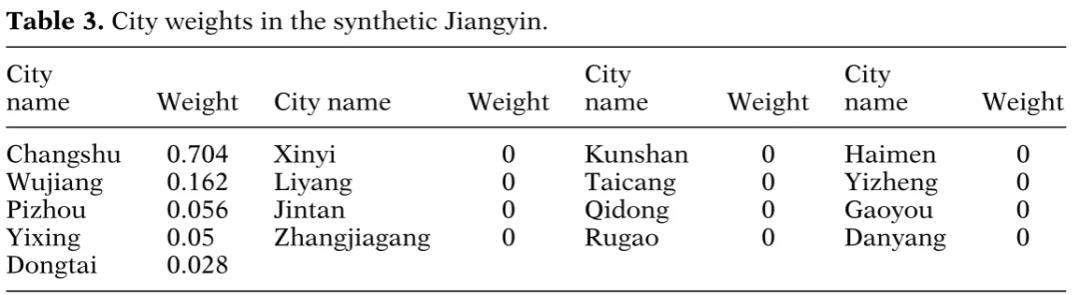
文章中的表3显示了构建合成江阴市的其他城市的贡献权重。很明显,常熟和吴江提供了最有用的信息,而邳州、宜兴和东台也做出了一定的贡献。因此,在公司层面的分析中,作者将这五个城市中的公司作为DiD分析的对照组。
三、实证过程
实证模型可以表示为



为了衡量企业能够在多大程度上自行筹集资金,作者按照Whited(2006)和Duchin, Ozbas和Sensoy(2010)的方法构建了如下指标,如式(3)所定义。作者进一步将企业划分为现金流流动性强弱划分:如果企业的指数高于中位数,则被划分为高流动性,否则被划分为低流动性。
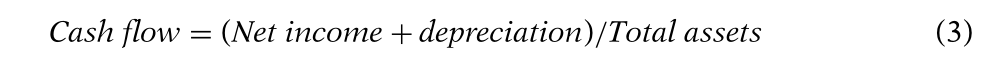
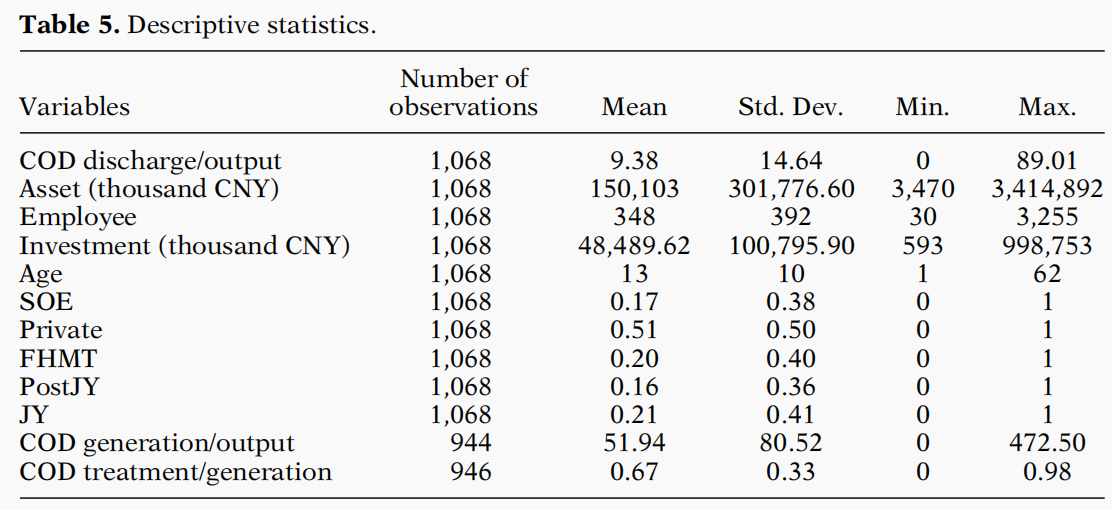
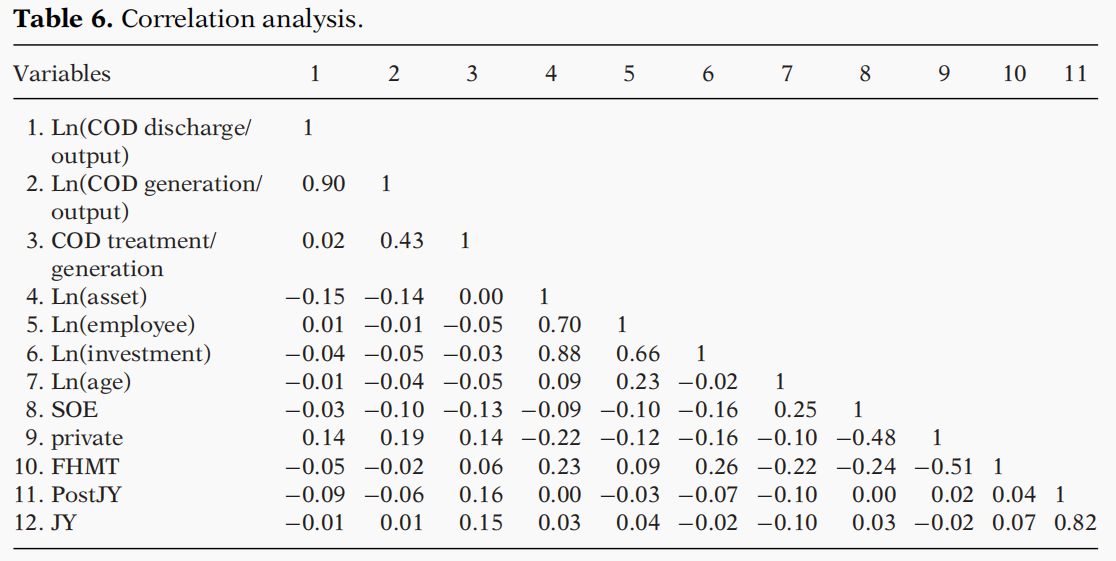
变量及其相关性的统计描述见文中的表5和表6。
文章中的表7-表9为实证结果。
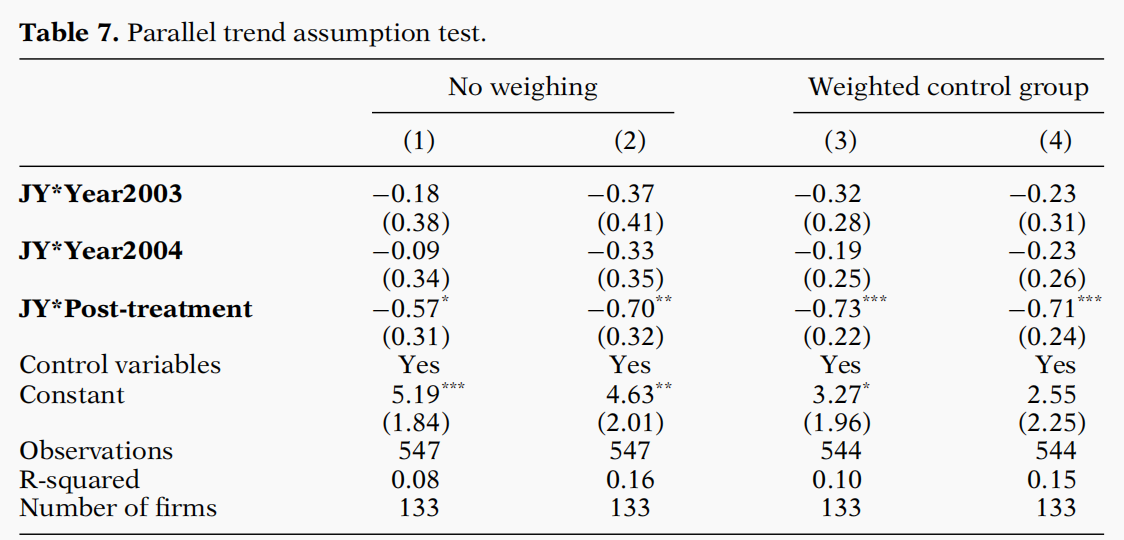
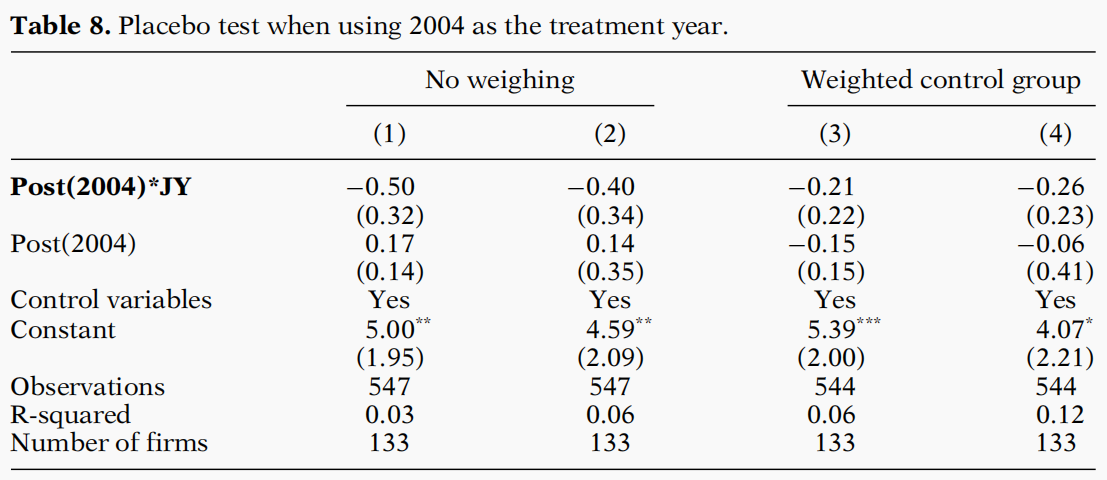
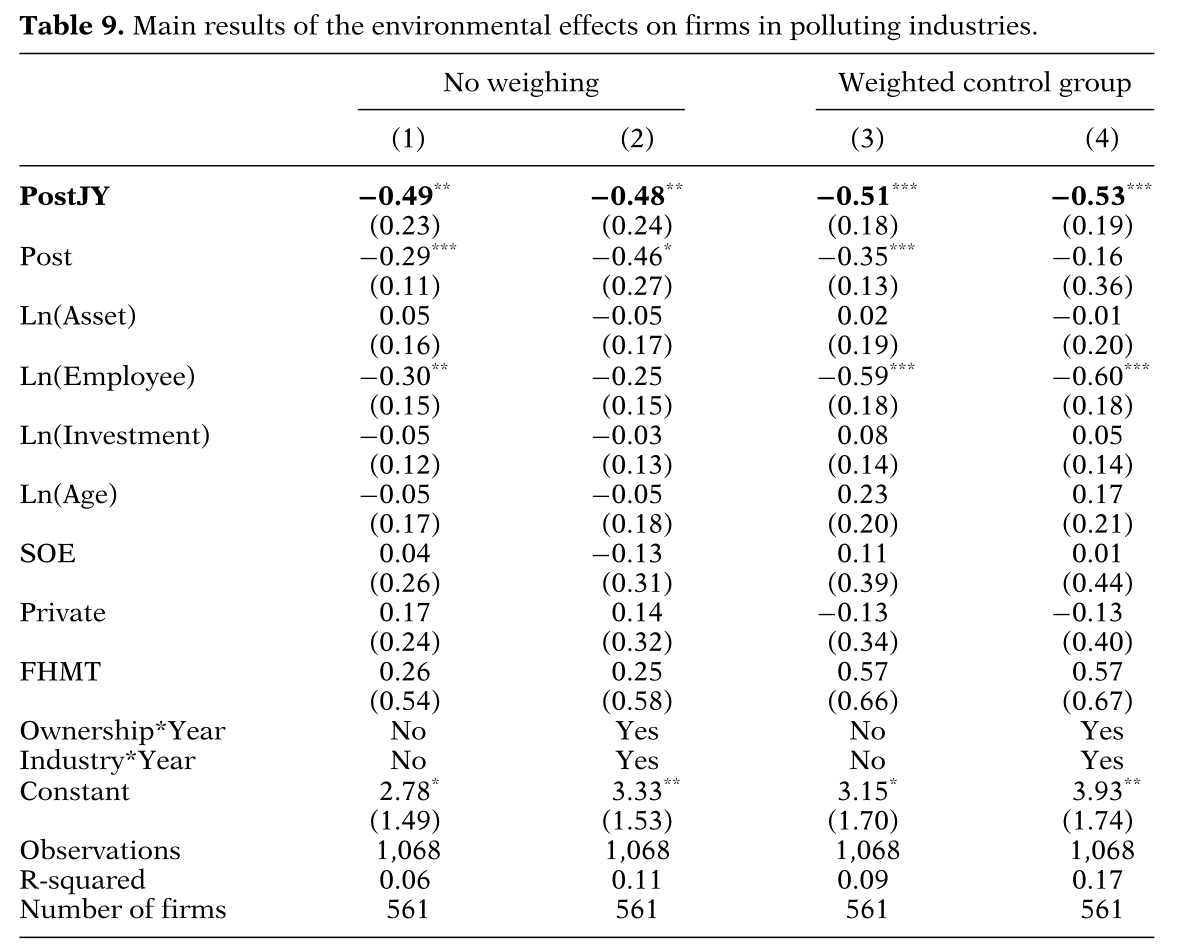
表9为DiD的回归结果,所有回归分析均采用固定效应模型,并以污染排放强度作为指标进行分析。第1和第2列的对照城市没有进行加权,而在第3和第4列,则根据合成控制法的权重对它们进行加权。
PostJY是本文最关心的变量,该变量的系数能够刻画江阴市绿色信贷政策的影响。表9显示,该变量的系数负向显著,由此可见,该政策的实施使得江阴市显著降低了污染排放强度。
四、结论
本文探究了中国绿色信贷政策对环境的影响。作者研究发现,绿色信贷政策的实施显著地激励了企业的污染排放强度。绿色信贷政策是一种金融发展过程中的政策创新,作者的研究提供的证据表明,这一政策将极大的调动了企业生产绿色化的积极性,有助于企业自觉减少污染排放。
原文摘要
This study examines the impact of China’s green credit policy on the environment. In particular, we consider an initiative that requires all banks to base their loan decisions on corporate environmental performance. This is an important issue since it is globally gaining popularity to leverage bank loans as an avenue to enforce corporate environmental responsibility. Moreover, there are only a handful of empirical investigations in relation to the impacts of credit constraint on corporate environmental behaviors and strategies. This research also provides useful insights on how to enhance environmental regulation enforcement, using the Environmental Protection Bureau in partnership with local banks to exert a creditable threat of financial constraint on unfavorable environmental outcomes. Using the synthetic control method and difference-in-differences analysis, we find that this policy has significantly motivated firms, particularly those firms with a higher dependence on external financing, to reduce water pollution. We further discover that the policy compels firms to favor pollution prevention at the source instead of end-of-pipe treatments, since the policy imposes a long-term credit constraint on pollution.
作者:
张蓦严中央财经大学金融学院博士研究生
指导老师:
王 遥中央财经大学绿色金融国际研究院院长
原创声明
如需转载、引用本文观点,请注明出处为“中央财经大学绿色金融国际研究院”。
新媒体编辑:杨颖安